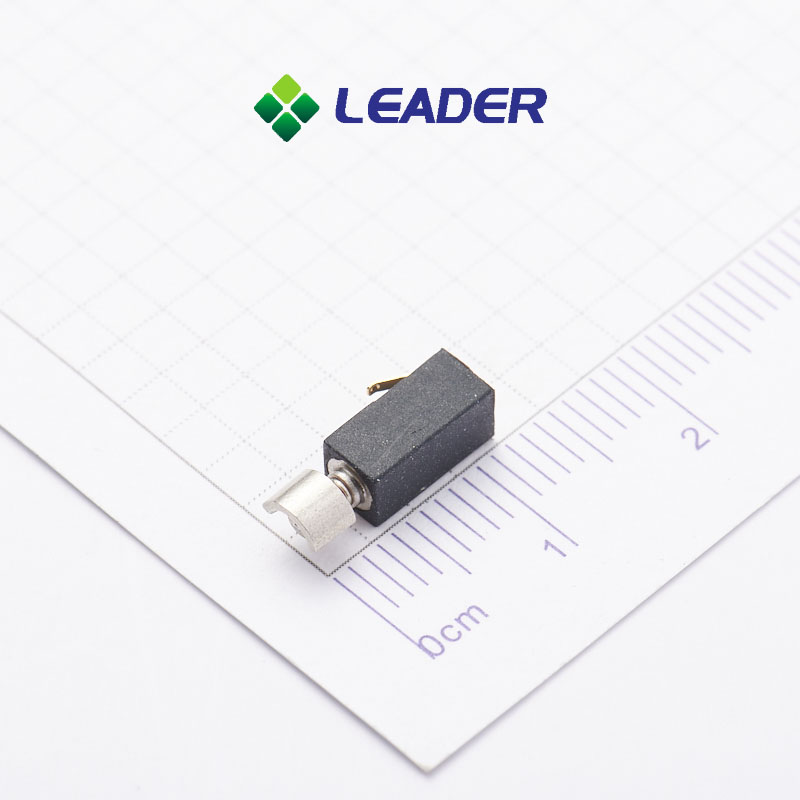
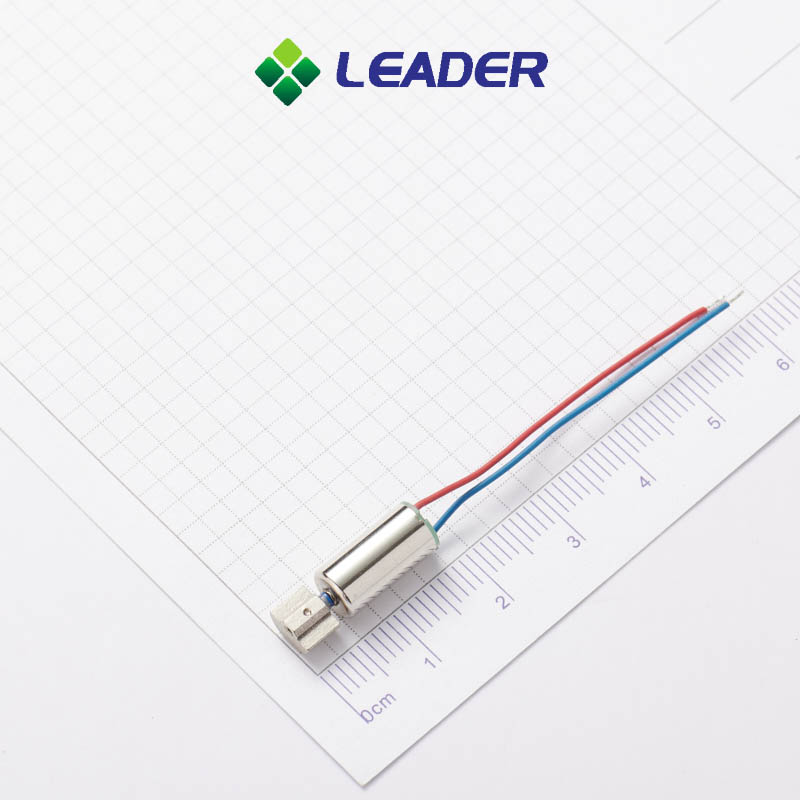
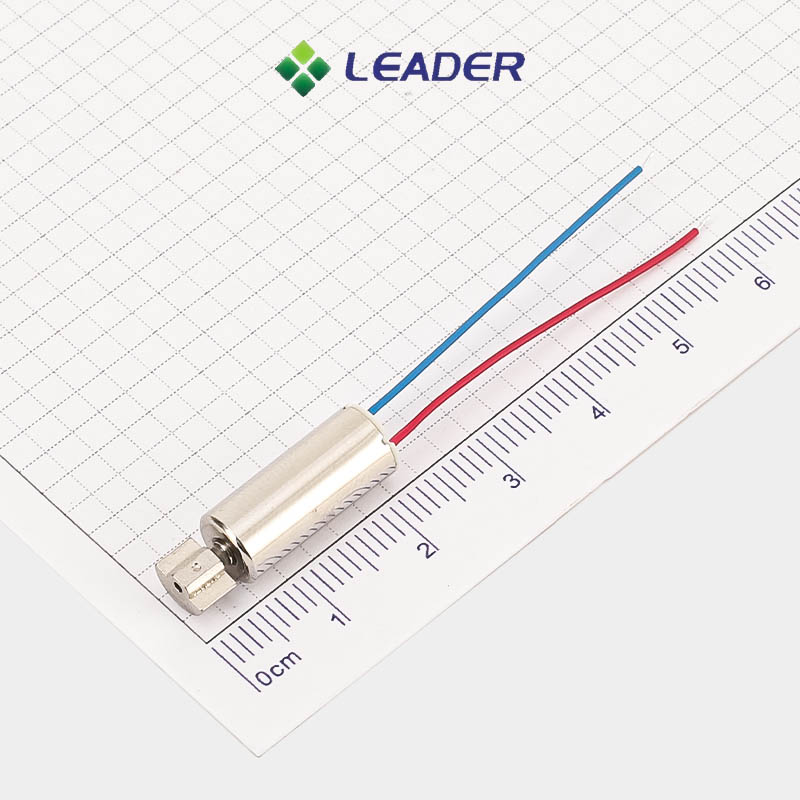
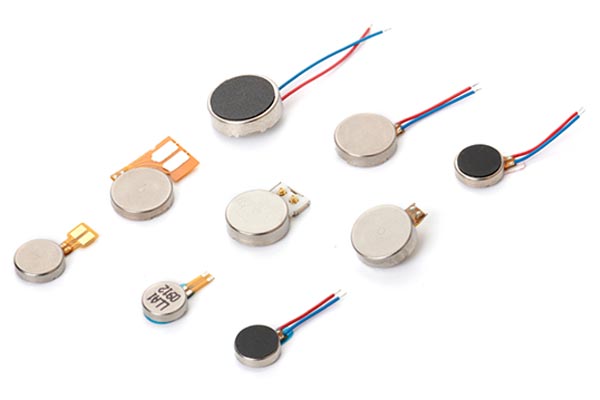
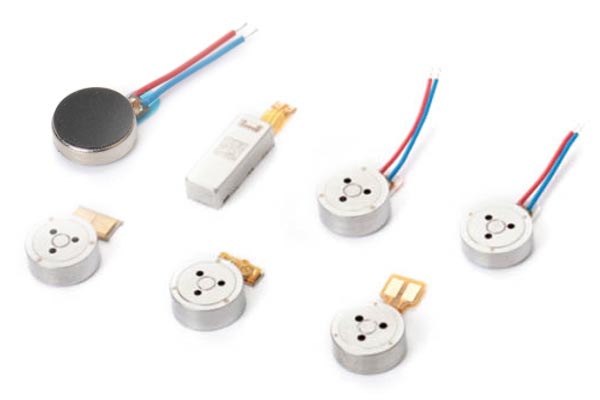
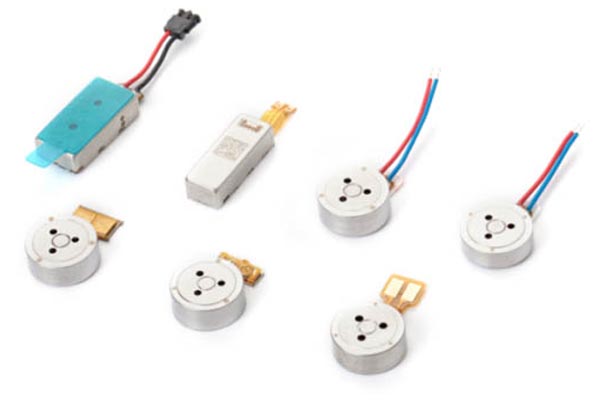
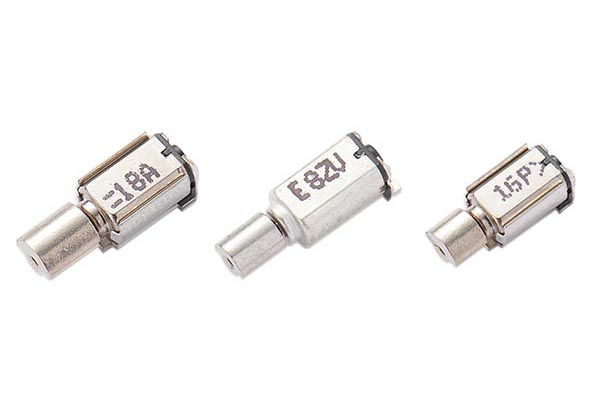
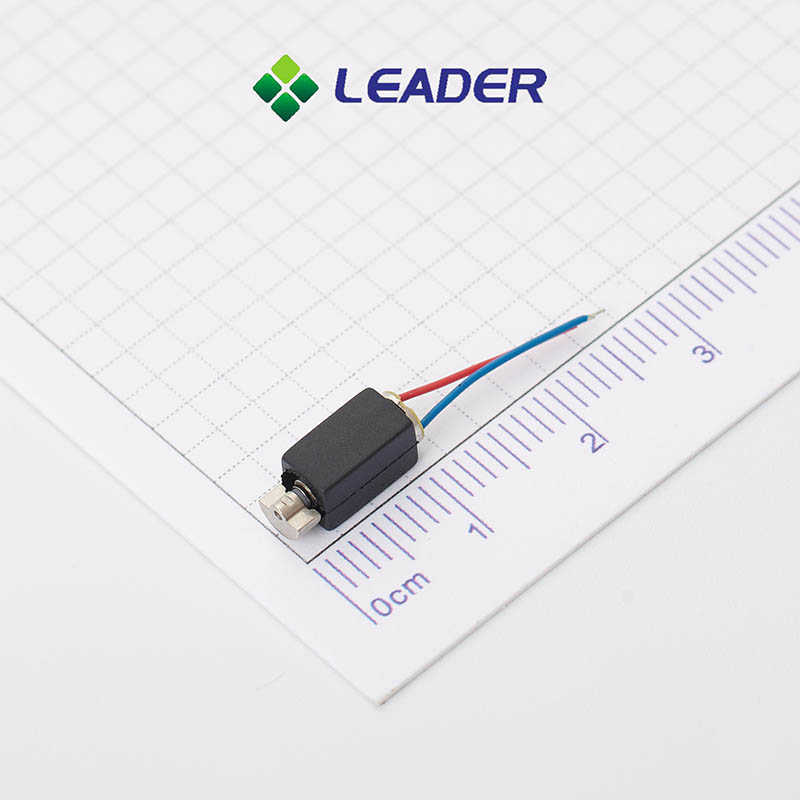
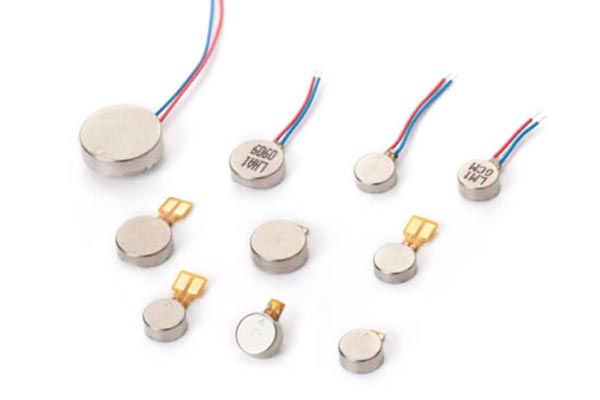
Leader-Motor: Your Trustworthy Coreless Dc Motor Manufacturer
At LEADER-Motor, we specialize in the production of high-quality coreless brush DC motors with diameters ranging from 3.2mm to 7mm. As a leading coreless DC motor factory, we take pride in providing top quality products with guaranteed quality. Our commitment to excellence is demonstrated by our ability to provide comprehensive specifications, data sheets, test reports, performance data and related certifications.
When you choose LEADER-Motor for your coreless motor needs, you can be assured of a quality product that meets your specific requirements. Please feel free to contact us to explore our range of high quality coreless electric motors.
What We Produce
The coreless motors (also known as cylindrical motor) is characterized by having a low startup voltage, energy-efficient power consumption and predominantly radial vibration.
Our company specializes in the production of coreless vibration motor with diameters ranging from φ3mm to φ7mm. We also offer customizable specifications to meet the specific needs of our clients and the ever-increasing demands of the market.
Shrapnel Type
| Models | Size(mm) | Rated Voltage(V) | Rated Current (mA) | Rated(RPM) | Voltage(V) |
| LCM0408 | ф4*L8.0mm | 3.0V DC | 85mA Max | 15000±3000 | DC2.7-3.3V |
| LCM0612 | ф6*L12mm | 3.0V DC | 90mA Max | 12000±3000 | DC2.7-3.3V |
| LCM0716 | ф7*L16mm | 3.0V DC | 40mA Max | 7000±2000 | DC1.0~3.2 |
Looking for compact and reliable solutions? Explore how our surface mount vibration motors offer precision and durability in small packages!
Still not finding what you're looking for? Contact our consultants for more available products.
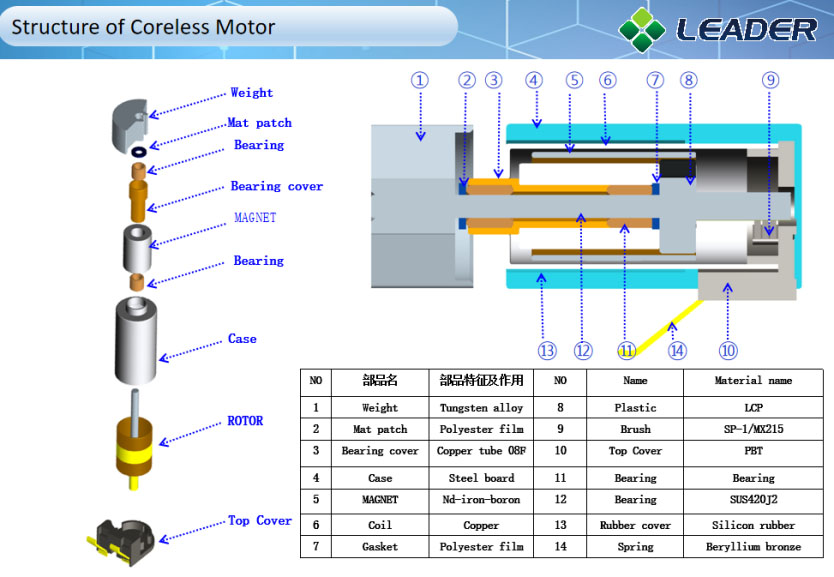
Structure of Coreless Motor:
Coreless brush dc motor consist of a rotor with wire windings (usually made of copper) and a stator with permanent magnets or electromagnetic windings.
The lightweight and flexible rotor structure enables faster dynamic response and increased efficiency, while the stator is designed to ensure a stable and consistent magnetic field for optimal motor performance.
Coreless Brushed DC Motors have excellent performance and are easier to control.
We provide three types of coreless brushed DC motors whose diameters are 3.2mm, 4mm, 6mm and 7mm, with hollow rotor design.
Application of Coreless Dc Motors
Coreless motors are typically used in products that require high precision, low noise and high speed. Some common applications include:
Gamepads
Coreless brush dc motor is used in gamepads to provide force feedback to the player, enhancing the gaming experience by providing tactile cues for actions, such as firing a weapon or crashing a vehicle.

Model airplanes
Coreless motors are used to small model aircrafts due to their lightweight and compact size. These small vibrating motor require low current and provide high power-to-weight ratios, enabling model airplanes to achieve high altitudes and speeds.

Adult products
Coreless dc motor may be used in adult products, such as vibrators and massagers, where a lightweight and high-precision motor is required. Additionally, coreless motors' low-noise operation makes them suitable for use in quiet environments.

Electric toys
Coreless dc motors are commonly used in miniature electric toys, such as remote-controlled cars and helicopters. The motors offer efficient and responsive control of the toy due to their high torque and low power consumption.

Electric toothbrushes
Coreless motors are used in electric toothbrushes, providing vibration that oscillates the brush head for effective cleaning of teeth and gums.
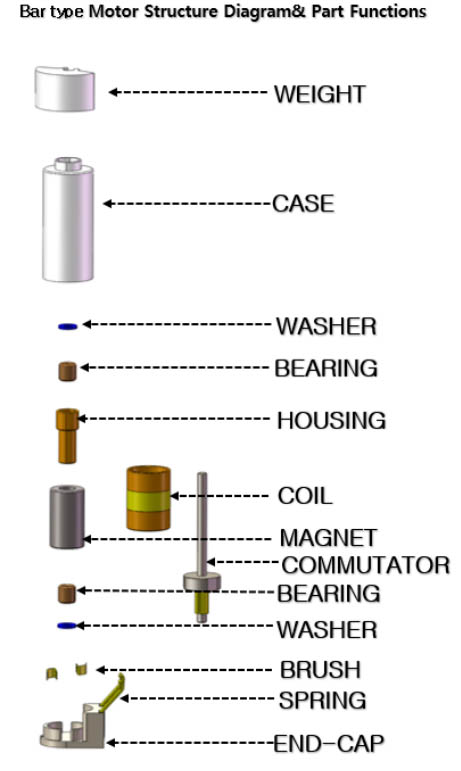
Why Use a Coreless Motor?
Working Principle
Coreless motors are characterized by the fact that there is no iron core in the rotor. Instead of a traditional iron core winding, the rotor in a coreless motor is wound with a lightweight and flexible material, such as copper wire. This design eliminates the inertia and inductance of the core, allowing faster acceleration, deceleration and precise speed control. Additionally, the absence of iron in the rotor reduces eddy currents, hysteresis losses and cogging, resulting in smoother, more efficient operation.
Advantages of coreless motors:
Improved efficiency: Coreless motors exhibit high energy efficiency due to reduced energy losses associated with hysteresis and eddy currents. This makes them an excellent choice for battery-powered devices and applications where energy conservation is critical.
High power-to-weight ratio: Coreless motors have a high power density relative to their size and weight, making them suitable for applications requiring compact and powerful motors, such as medical equipment, robotics, and aerospace equipment.
Precise and smooth Operation: The absence of an iron core in coreless motors reduces cogging and allows for smoother, more precise motion, making it ideal for applications that require high flexibility and accuracy, such as cameras, robotics and Prosthetic equipment.
Disadvantages of coreless motors:
Higher cost: The unique structure and materials used in coreless motors make them more expensive to manufacture than traditional iron-core motors.
Heat dissipation: Coreless motors may be slightly less capable of dissipating heat due to the absence of an iron core, requiring careful consideration of thermal management in some applications.
Main Soldering Modes of Coreless Motor:s
Here are some detailed descriptions of the main soldering modes used in coreless motors.
1. Leade Wire: Lead wire is a commonly soldering mode in coreless motors. It uses specialized equipment to attach a metallic wire to the electrode pads on the motor housing. Wire soldering provides a reliable and robust electrical connection that allows for precise control and operation of the motor.
2. Spring Contact: Spring contact is another soldering mode used in coreless motors. It uses a metal spring clip to establish an electrical connection between the motor wires and the power source. Spring contact is easy to manufacture and provides a relatively strong electrical contact that can withstand vibration and mechanical shock.
3. Connector Soldering: Connector soldering involves attaching a connector to the motor housing which use a high-temperature soldering process. The connector provides an easy-to-use interface for connecting the motor to other parts of the device. This method is commonly used in electric toothbrushes and other battery-powered devices.
Overall, these three soldering modes are commonly used in coreless motors. Each offers unique benefits in terms of electrical connection reliability, mechanical robustness and ease of use. LEADER will typically choose the most appropriate method of soldering based on the requirements of end products.
Get Coreless Motors in Bulk Step-by-step
Coreless Motors FAQ From Coreless Dc Brush Motor Manufacturers
A coreless vibration motor possesses an inner core made from iron, with coils that are weaved tightly around this inner core, with the rotor made of dense iron layers. A coreless DC motor will not have this inner iron core component, hence its name – coreless.
The operating voltage range for coreless motor is typically between 2.0V to 4.5V, but this may vary depending on the specific motor model and design.
Coreless motors have multiple advantages: high efficiency, low heat generation, low noise, precise control and quick acceleration. They are ideal for use in portable and battery-powered devices due to their low voltage start-up and power consumption.
No, coreless motors are not waterproof. Prolonged exposure to moisture or water can damage the motor and affect its efficiency. If needed, LEADER can customize waterproof covers according to customer requirements.
Dc coreless motor is maintenance-free, but proper handling, installation and usage practices are required to ensure optimal performance. Specifically, users are advised to avoid overloading, temperature extremes and moisture exposure.
There are several differences between coreless DC motors and traditional DC motors (which usually have an iron core) that need to be considered when choosing the right motor for a specific application:。
1. Structure: Coreless DC motor designs lack the iron core found in traditional motors. Instead, they have coil windings that are usually wound directly around the rotor. A conventional DC motor has a rotor with an iron core that provides a flux path and helps concentrate the magnetic field.
2. Inertia: Since the coreless DC motor has no iron core, the rotor inertia is low and it can achieve faster acceleration and deceleration. Traditional iron-core DC motors typically have high rotor inertia, which affects the motor's ability to respond to changes in speed and direction.
3. Efficiency: Due to their design and construction, coreless DC motors tend to have higher efficiency and better power-to-weight ratio. Due to core-related losses, conventional DC motors may have lower efficiency and lower power-to-weight ratio, especially at smaller sizes.
4. Reversal: Coreless DC motors may require more complex commutation systems, such as electronic commutation using sensors or advanced control algorithms, to ensure precise, smooth operation. Conventional DC motors with an iron core may use a simpler brush commutation system, especially in smaller and less complex applications.
5. Dimensions and weight: Coreless DC motors are generally more compact and lighter than conventional DC motors, making them suitable for applications where size and weight are critical.
6. Cost: Coreless DC motors can be more expensive to manufacture due to the specialized winding techniques and materials required for their construction. Conventional DC motors with iron cores may be more cost-effective, especially in larger sizes and standardized applications.
Ultimately, the choice between coreless DC motors and conventional DC motors depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as performance, size constraints, cost considerations, and the need for precise motion control. Both types of motors have unique advantages and limitations that require careful evaluation to select the most appropriate option for a specific use case.
When choosing a cylindrical motor, you need to consider the following factors:
-Size and Weight: Determine the size and weight limits required for your application. Coreless motors come in a variety of sizes, so choose one that fits your space constraints.
-Voltage and current requirements: Determine the voltage and current limits of the power supply. Make sure the motor's operating voltage matches your power supply to avoid overloading or poor performance.
-Speed and torque requirements: Consider the speed and torque output required from the motor. Choose a motor with a speed-torque curve that meets your application needs.
-Efficiency: Check the efficiency rating of a motor, which indicates how efficiently it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. More efficient motors consume less power and generate less heat.
-Noise and Vibration: Evaluate the level of noise and vibration produced by the motor. Coreless motors generally operate with lower noise and vibration, but check product specifications or reviews for any specific noise or vibration characteristics.
-Quality and Reliability: Look for motors from reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality and reliable products. Consider factors like warranty, customer reviews, and certifications.
-Price and Availability: Compare prices from different suppliers to find a motor that fits your budget. Make sure the motor model you choose is readily available or has an adequate supply chain to avoid procurement delays.
-Application Specific Requirements: Consider any specific requirements unique to your application, such as special mounting configurations, custom shaft lengths, or compatibility with other components.
A: Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart home systems will enable micro coreless motors to be remotely controlled and synchronized with other devices.
B. The growing micro-mobility sector, including electric scooters and micro-vehicles, provides opportunities for coreless motors to power these portable transportation solutions.
C. Advances in materials and manufacturing technology will improve the performance and efficiency of micro coreless motors.
D. By using advanced algorithms, micro coreless motors can achieve enhanced motion control and accuracy, allowing for more precise and complex applications.
Coreless motors are lightweight, affordable, and don't operate quietly. A plus point is that they can run on cheap fuel, which makes them an overall cost-effective choice. Brushless motors are considered to offer greater efficiency and are therefore the preferred choice for automation and healthcare applications.
Consult Your Leader Experts
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your coreless motors need, on-time and on budget.