Recall how a brush DC motor works
For a better understanding of how brushless motors work, we must first recall how a brush DC motor works, as they were used for some time before brushless DC motors were available.
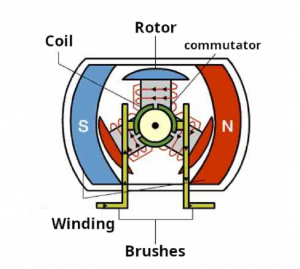
In a typical DC motor, there are permanent magnets on the outside and a spinning armature on the inside. The permanent magnets are stationary, so they are called the stator. The armature rotates, so it is called the rotor. The armature contains an electromagnet. When you run electricity into this electromagnet, it creates a magnetic field in the armature that attracts and repels the magnets in the stator. The commutator and the brushes are the primary components that differentiate the DC brush motor from other kinds of motors.
What is Brushless DC Motor?
A brushless DC motor or BLDC is an electric motor powered by direct current and generates its motion without any brushes like in conventional DC Motors.
Brushless motors are more popular nowadays than conventional brushed DC motors because they have better efficiency, can deliver precise torque and rotation speed control, and offer high durability and low electrical noise, thanks to the lack of brushes.
How Do Brushless DC Motors Work?
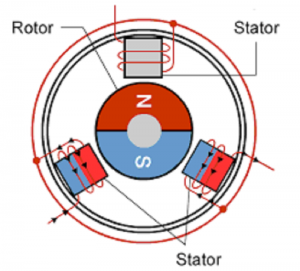
The working principle of a micro brushless motor involves the interaction of a rotating magnet and a stationary coil. Unlike traditional brushed motors, there are no physical brushes or commutators involved. In a brushless motor, a rotor consisting of permanent magnets rotates around a stationary stator containing multiple coils or windings. These coils are placed around the stator at specific spatial intervals. The motor's electronics control the current flowing through each coil to create a rotating magnetic field. This rotating magnetic field interacts with permanent magnets on the rotor, causing the rotor to rotate. The direction and speed of rotation can be controlled by adjusting the time and magnitude of the current flowing through the coil. For smooth rotation, position sensors are often integrated into the motor to provide feedback to the control circuit. This feedback enables the motor controller to accurately determine the position of the rotor and adjust the current in the coils accordingly. Overall, micro brushless motors operate using the interaction between the rotating magnetic field generated by the stator coils and the permanent magnets on the rotor, allowing efficient and precise rotation without the need for physical brushes or commutators.
Conclusion
Micro brushless motors have high efficiency, long lifespan, precise control, and reduced noise compared to traditional motors. They are widely used in various industries, including aerospace, medical equipment, robotics, and consumer electronics. As the technology and demand for precise motor control continue to grow, the use of micro brushless motors is expected to increase in the future.
Consult Your Leader Experts
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your micro brushless motor need, on-time and on budget.
Post time: Aug-25-2023