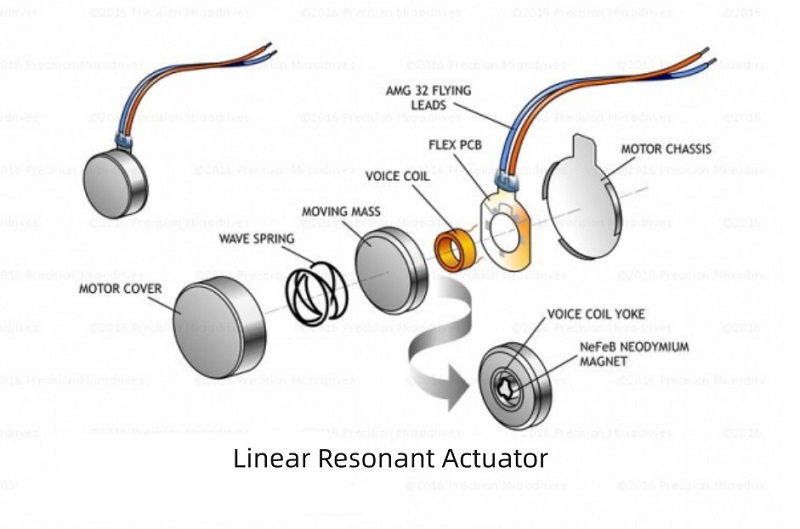
What are linear resonance actuators?
A Resonant Actuator (LRA) is a vibration motor that generates an oscillating force on a single shaft. Linear resonant actuators differ from DC eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors. LRA motors require AC voltage to power the voice coil, which is in contact with a movable mass connected to a spring. When the voice coil is driven at the resonance frequency of the spring, the entire actuator vibrates with a perceivable force. While the frequency and amplitude of a linear resonant actuator can be modified by adjusting the AC input, the actuator needs to operate at its resonant frequency in order to generate significant force with high currents.
There are several reasons why LRAs may be preferred haptic vibrators in some designs:
- Linear resonant actuators (LRAs) has a longer lifespan because there are no internal brushes to wear out. This effectively makes them brushless, although the springs may fatigue over time.
-Linear resonant actuators (LRA) typically provide enhanced tactile performance with minimal hysteresis and fast rise times, which are critical for simulating short duration – high frequency tasks such as keyboard switches for typingswitches.
-LRA motors consume lower power than ERM equivalents.
- Linear motors have Compact size.
- The input signal’s amplitude and frequency are independent of each other, allowing the input to have a more complex waveform than with an ERM. This can produce a ‘richer’ user haptic experience.
Consult Your Leader Experts
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your micro brushless motor need, on-time and on budget.
Post time: May-18-2024